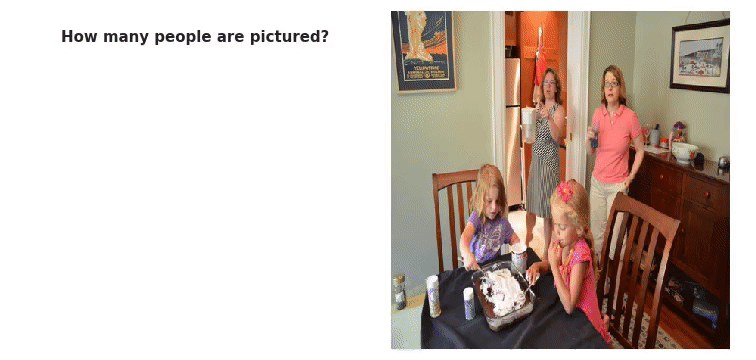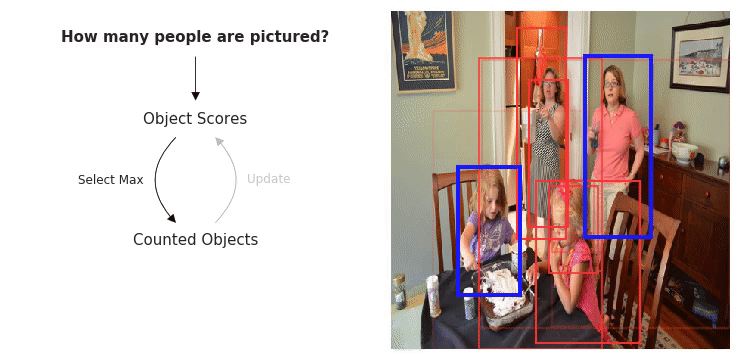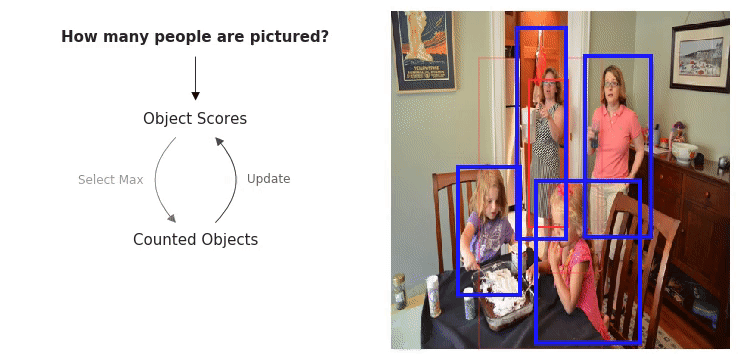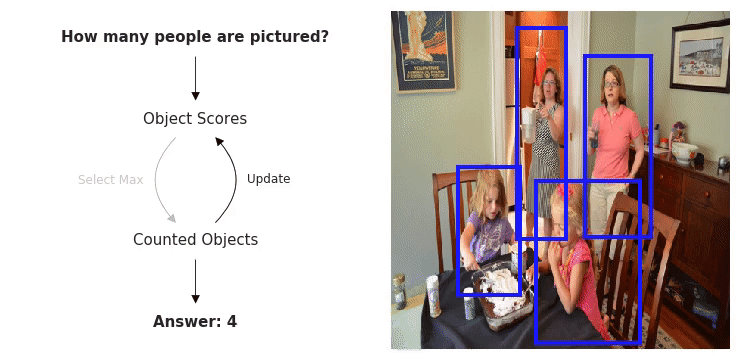The WikiText Long Term Dependency Language Modeling Dataset
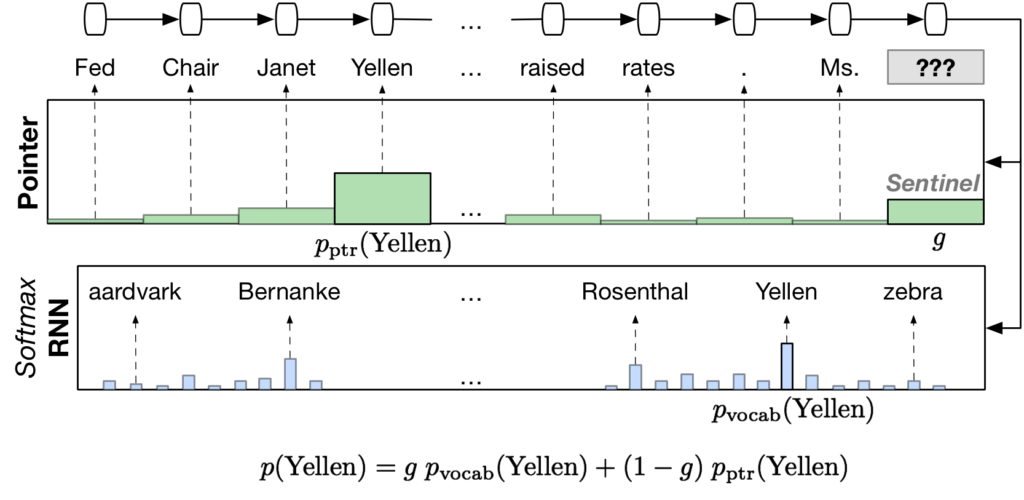
The WikiText language modeling dataset is a collection of over 100 million tokens extracted from the set of verified Good and Featured articles on Wikipedia. The dataset is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Compared to the preprocessed version of Penn Treebank (PTB), WikiText-2 is over 2 times larger and WikiText-103 is over 110 […]
The WikiText Long Term Dependency Language Modeling Dataset Read More »