AI is advancing so rapidly that the infrastructure that supports it can’t always keep up. Last year, we saw this firsthand when a critical latency issue caused 20-second delays for some agent responses. That’s a lot of lag for anyone, especially an enterprise, so the Agentforce team quickly triggered a “code red.”
Over the course of six months, our team delivered more than 30 system-wide enhancements touching nearly every facet of the Agentforce 360 Platform and its underlying infrastructure. The end result was an astounding 70% reduction in latency. Here’s how we got there.
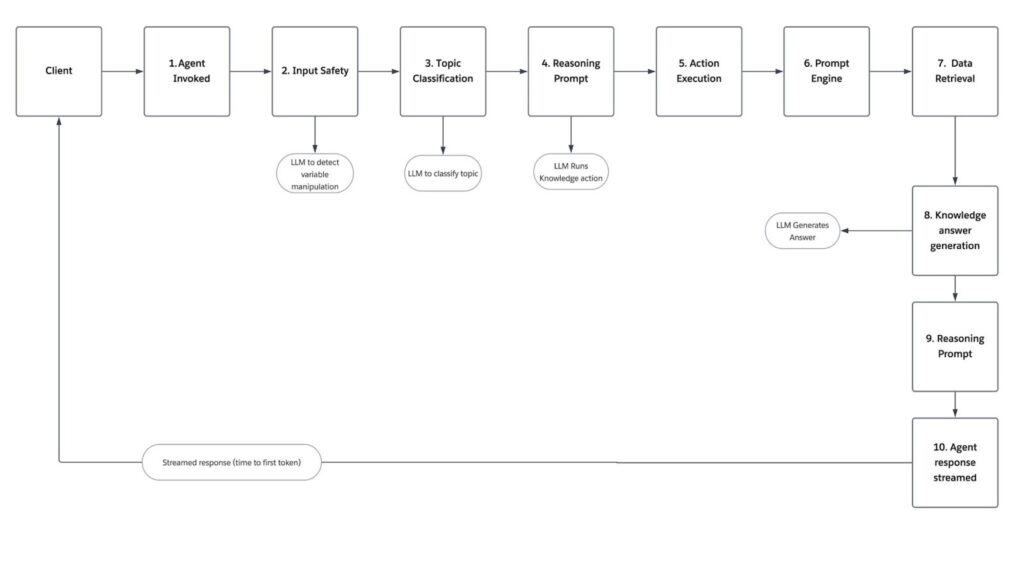
How Agentforce used to work
To achieve such a dramatic boost in performance, we went back to the drawing board and scrutinized each step of the Agentforce runtime. Previously, whenever a user invoked an agent, Agentforce would follow these steps:
- Agent invoked: The process begins when the client initiates an interaction, triggering the agent workflow.
- Input safety: The Einstein Trust Layer and system guardrails are activated to analyze the user’s input. An LLM scans for prompt injections, toxicity, and variable manipulation to ensure the request is safe to process.
- Topic classification: The system evaluates the message context to categorize it. Another LLM verifies if the request matches an existing topic.
- Reasoning prompt: The agent assembles context, scope and history to kickoff the decision-making action loop. We call another LLM to generate the specific input required to execute a knowledge action.
- Action execution: The system executes the appropriate tool or process to begin gathering necessary information.
- Prompt engine: This component manages all LLM interactions throughout the retrieval process.
- Data retrieval: Specialized retrievers query Data Cloud 360 to fetch the data needed to fulfill the request.
- Knowledge answer generation: The system synthesizes the retrieved data into a coherent answer, ensuring the response is grounded in your specific business data.
- Reasoning prompt: An LLM reviews the generated answer to verify if the answer accurately addresses the user’s question before it’s finalized.
- Agent response streamed: The validated response is streamed back to the client, completing the loop.
As pictured below, this process involved four LLM calls before a response was streamed out to the user.

Streamlining the runtime
So, how did we get to that 70% reduction in latency? Here’s a look at the revised Agentforce runtime.

The solution involved a multi-pronged approach that touched every level of our architecture.
- Refactoring and optimizing the AI stack: From action execution to the way Agentforce interprets and runs prompts, our team refactored and optimized core software components and key code paths, delivering more than 30 system-wide improvements.
- Architectural improvements: To enable faster agent responses, we made a number of optimizations to the Atlas Reasoning Engine and the way Agentforce executes actions, particularly knowledge lookups for unstructured data. This architectural change, as shown below, consolidates the number of LLM calls the system makes before streaming an output from four to two, reducing time-to-first-token, a key latency metric.
- Enhanced input safety: We replaced LLM-based input safety screening with an enhanced framework to guard against prompt injection attacks. The framework allows agent authors to create deterministic rule filters for sensitive topics. Authors can also chain variables from one action to another without exposing the variables to the LLM, therefore safeguarding the data against prompt injection manipulation attempts.
- Optimized topic classification: We replaced a general-purpose LLM with HyperClassifier, our own specialized Small Language Model (SLM). Unlike standard models that generate free-form text, we trained HyperClassifier to perform single-token prediction, outputting a unique token representing a specific topic class. This innovation resulted in a 30x speedup for topic classification, while matching the accuracy of larger models.
- Infrastructure and scaling: We increased our scaling capacity by switching to OpenAI’s Scale Tier, which offers premium latency, uncapped scale and higher reliability. This will help ensure that as Agentforce grows, our latency remains consistently low.
In summary, our new architecture reduces the overall number of steps in the Agentforce runtime and consolidates the number of LLM calls in half before the end-user sees the first token of the response. Together, these optimizations deliver a 70% reduction in latency.
Keeping latency low
To maintain these gains and prevent future slowdowns, we’re continuing to invest in a range of solutions, such as comprehensive dashboards, performance profiling for individual components, and identifying end-to-end and component-level regressions in latency. Our dashboards allow us to monitor aggregate latency trends for our agents, along with drilling down on outlier agents with high latencies. Furthermore, our dashboards allow our engineers to drill down into component-level metrics such as input/output tokens used, LLM processing time, and time taken for data retrieval. Finally, we have set up an alarm to alert for latency regressions, enabling organizations to respond immediately.

This continuous monitoring ensures that the speed improvements we’ve won are improvements we keep. We remain committed to continuous performance and innovation and ensuring Agentforce sets the standard for agentic speed and reliability.